151/25 Pakistan's Global Academic Standing Positive Trends: A Historical Analysis of QS University Rankings
Posted 6 months ago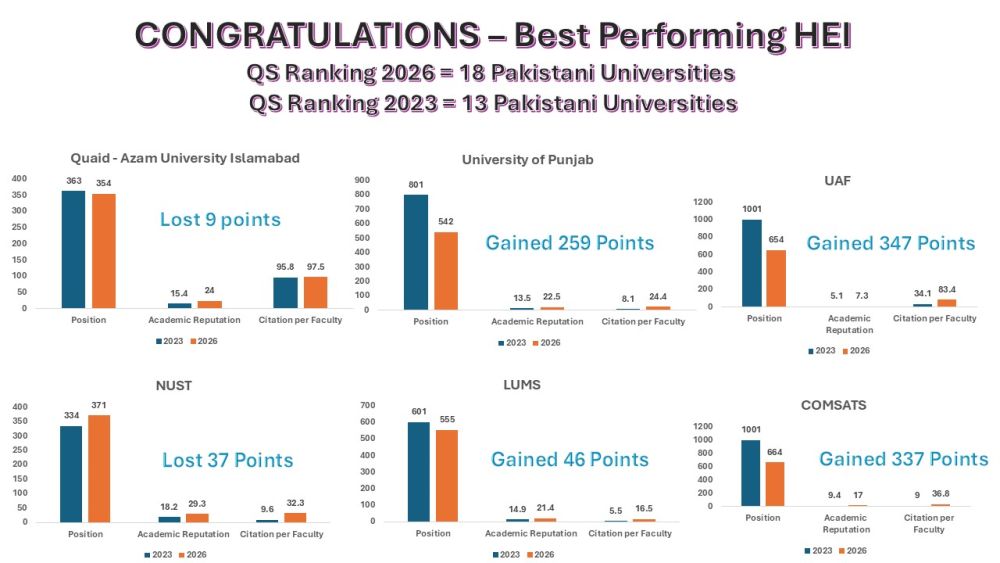
By: Professor Dr. Muhammad Mukhtar - July 5, 2025
Executive Summary:
Over the past two decades, Pakistani universities have demonstrated consistent progress in global higher education metrics, particularly the QS World University Rankings. This trajectory of improvement results from targeted policy interventions, institutional reforms, and a growing culture of academic excellence. The rising visibility of Pakistani institutions in the QS rankings reflects the country's commitment to quality education, research, and international engagement.
1. Introduction
The QS World University Rankings, published annually by Quacquarelli Symonds (UK), have emerged as a leading global benchmark for assessing institutional performance. Using indicators such as academic reputation, research impact, internationalization, and teaching quality, these rankings significantly influence global perceptions of university excellence.
Pakistan's representation in these rankings used to be minimal. However, a strategic and systemic transformation has enabled the country to strengthen its global academic footprint.
2. Early Years: Modest Beginnings (2006- 2010)
In the early 2000s, only a few Pakistani universities, most notably Quaid-i-Azam University and the University of the Punjab, made it to the QS rankings, and even then, at lower tiers.
Key challenges barring ranking during this period included:
- Limited research publications in indexed journals
- Low international visibility and collaboration
- Inadequate faculty-student ratios and infrastructure
- Modest citation impact
This phase marked the realization of the need for comprehensive reforms in higher education.
3. The Reform Era: Strategic Interventions (2010 - 2020)
Under the leadership of the Higher Education Commission, Federal Ministry of Education and Professional Training, long-term reforms were implemented. These reforms continued initial efforts, and one could easily say that they were based on a well-orchestrated structure. These included:
- Strengthening postgraduate research programs
- A well-orchestrated Foreign Faculty Hiring Program
- Launching overseas PhD faculty development schemes
- Promoting international collaborations and joint ventures
- Expanding access to digital libraries and research tools
- Establishing Quality Enhancement Cells (QECs) in universities
As a result, universities such as the National University of Sciences and Technology (NUST), Lahore University of Management Sciences (LUMS), and COMSATS University Islamabad began to show significant upward mobility in QS rankings, regionally and globally.
4. Post-2020: Acceleration and Recognition
Between 2020 and 2025, Pakistan witnessed its highest number of universities featured in QS Rankings across multiple categories:
- 13 Pakistani universities were ranked globally in the QS World University Rankings 2023 that number have risen to 18 in the current ranking.
- Over 30 universities featured in the QS Asia University Rankings 2025.
- Several institutions appeared in QS Subject Rankings, including engineering, business, agriculture, and pharmacy.
5. Enablers of Success
Key factors contributing to the improved rankings include:
- Research Productivity: Enhanced publication output and citation impact through faculty incentivization.
- Academic Reputation: Increased visibility via international conferences, partnerships, and alumni networks.
- Institutional Governance: Strengthening quality assurance and strategic planning across public and private universities.
- Student Outcomes: Employer confidence in graduates is growing, as reflected in QS's employer reputation metric.
6. Challenges and Gaps
Despite measurable progress, Pakistani universities face several systemic challenges:
- Low International Faculty and Student Ratio: Affects rankings and limits global academic exchange.
- Research Funding Constraints: Many institutions still have inadequate resources for high-impact research.
- Brain Drain: Retaining top faculty remains difficult due to global mobility and competitive offers abroad.
- Limited Performance in QS Sustainability Rankings: There is an urgent need to address institutional contributions to environmental and social impact.
7. Recommendations for Policy and Institutional Strategy
To sustain and accelerate this progress, the following national-level actions are recommended:
- Develop a National QS Ranking Strategy: Establish a dedicated task force to guide institutions in aligning with global performance metrics.
- Invest in Internationalization: Incentivize recruitment of international faculty and student mobility programs.
- Improve Research Ecosystem: Increase funding for competitive research, innovation hubs, and publication support.
- Adopt Sustainability and Social Impact Metrics: Encourage universities to participate in QS Sustainability Rankings through initiatives on climate action, gender equality, and community engagement.
- Benchmarking and Transparency: Create a national dashboard for tracking university performance across international ranking systems.
The historical elevation of Pakistani universities in QS Rankings symbolizes progress and a call to action. It showcases Pakistan's potential to emerge as a regional academic hub, provided institutional growth matches national commitment and global ambition.
As Pakistan positions itself in the knowledge economy, its universities must be equipped to teach curricular aligning with job markets and do research benefitting the region, not just to lead.





